Digital currencies and distributed ledgers are an innovation that could have a range of impacts on many areas, especially on payment systems and services, said a report published by Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
These impacts could include the disruption of existing business models and systems, as well as the emergence of new financial, economic and social interactions and linkages.
Even if the current digital currency schemes do not persist, it is likely that other schemes based on the same underlying procedures and distributed ledger technology will continue to emerge and develop.
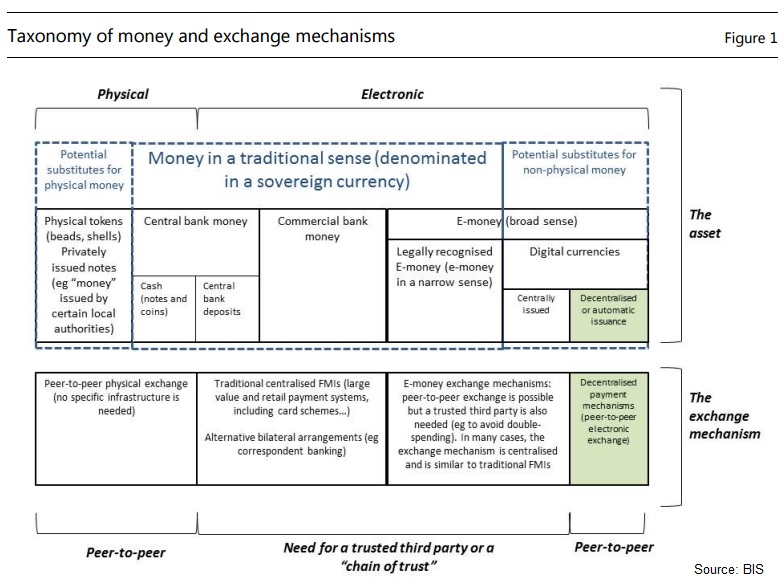
The asset aspect of digital currencies has some similarities with previous analysis carried out in other contexts (eg there is analytical work from the late 1990s on the development of e-money that could compete with central bank and commercial bank money).
However, unlike traditional e-money, digital currencies are not a liability of an individual or institution, nor are they backed by an authority.
Furthermore, they have zero intrinsic value and, as a result, they derive value only from the belief that they might be exchanged for other goods or services, or a certain amount of sovereign currency, at a later point
in time.
Accordingly, holders of digital currency may face substantially greater costs and losses associated with price and liquidity risk than holders of sovereign currency.
The genuinely innovative element seems to be the distributed ledger, especially in combination with digital currencies that are not tied to money denominated in any sovereign currency.
The main innovation lies in the possibility of making peer-to-peer payments in a decentralised network in the absence of trust between the parties or in any other third party.
Digital currencies and distributed ledgers 18 CPMI report on digital currencies are closely tied together in most schemes today, but this close integration is not strictly necessary, at least from a theoretical point of view.
This report describes a range of issues that affect digital currencies based on distributed ledgers.
Some of these issues may work to limit the growth of these schemes, which could remain a niche product even in the long term. However, the arrangements also offer some interesting features from both demand
side and supply side perspectives.
These features may drive the development of the schemes and even
lead to widespread acceptance if risks and other barriers are adequately addressed.
There are different ways in which these systems might develop: either in isolation, as an alternative to existing payment systems and schemes, or in combination with existing systems or providers.
These approaches would have different implications, but both could have significant effects on retail payment services and potentially on FMIs. There could also be potential effects on monetary policy or
financial stability.
However, for any of these implications to materialise, a substantial increase in the use of digital currencies and/or distributed ledgers would need to take place.
Central banks could consider – as a potential policy response to these developments – investigating the potential uses of distributed ledgers
in payment systems or other types of FMIs.
See the report here

